Abstract
Background: With the advent of several new agents in the treatment of multiple myeloma, including proteasome inhibitors (PIs), immunomodulatory drugs (IMiDs), and anti-CD38 monoclonal antibodies (mAb), the overall survival (OS) has significantly improved in the past two decades. However, most patients become refractory to currently available therapies along the disease trajectory. The median OS in triple-class-refractory patients (i.e., anti-CD 38 mAb, PIs, and IMiDs) is 6 months (Gandhi et al. Leukemia. 2019). Although BCMA-targeted therapies are a major advance in such patients, none of them are curative thus far, with the median progression-free survival (PFS) ranging from 3 months in BCMA-antibody drug conjugates (ADCs) to approximately 1 year in BCMA chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR T-cell) therapies. Furthermore, unique toxicities of BCMA-targeted agents such as ocular toxicity (ADCs), cytokine release syndrome, or neurotoxicity (CAR Ts and BiTEs) may preclude their use in many patients. Hence, there is a critical unmet need in patients with triple-class-refractory myeloma.
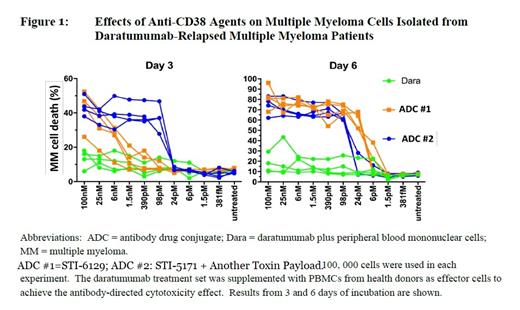
The STI-6129 ADC is produced by conjugating STI-5171, a fully human anti-CD38 mAb, with a covalently bound tubulin inhibitor, duostatin 5.2 (DUO-5.2), using a proprietary linker technology with a 3:1 drug-antibody ratio. STI-6129 binds to different CD38 epitopes than daratumumab. Upon binding to CD38, STI-6129 ADC is internalized by the cancer cell and undergoes lysosomal degradation, releasing DUO-5.2. This in turn leads to G2-phase cell cycle arrest, followed by caspase 3/7-dependent apoptosis and cell death. In studies on cynomolgus monkeys, the serum level of DUO-5.2 remained undetectable at all doses except at the highest dose of 4.5 mg/kg, indicating low likelihood of off-target toxicity. In vitro studies of primary human plasma cells, human tumor models, and animal xenograft models have demonstrated target elimination of CD38-positive human plasma cells by STI-6129. Importantly, STI-6129 has demonstrated cytotoxic activity in human multiple myeloma cells isolated from daratumumab-refractory patients (Figure 1). Hence, further investigation on clinical activity of STI-6129 is warranted.
Study Design: The 38-ADC-RRMM-101 study is a two-stage, multicenter, open-label, dose-finding phase 1/2 trial. The phase 1 trial is designed to identify the recommended phase 2 dose (RP2D) of STI-6129 by assessing safety, preliminary efficacy, and pharmacokinetics in patients with relapsed/refractory (RR) myeloma. The phase 2a stage of the trial will be a single-arm study to investigate the efficacy of STI-6129 in an expansion cohort of RR myeloma patients. Up to 25 patients will be enrolled in the phase 1 stage and 30 in the phase 2 stage of the study. The key inclusion criteria are the following: (a) RR myeloma with at least 3 prior lines of therapy in addition to being refractory to at least 1 PI, 1 IMiD, and 1 anti-CD 38 mAb; (b) measurable disease. The key exclusion criteria are: (a) receipt of the last dose of any anti-CD mAb within 90 days; (b) grade ≥3 neuropathy or grade 2 neuropathy with pain; (c) current history of CTCAE grade 3 muscle paresis, eyelid conditions, glaucoma, or any other ocular disorder that is CTCAE grade 2; (d) estimated creatinine clearance <60 ml/min; (e) left ventricular ejection fraction<40%. The primary endpoint of phase 1 stage of the study is safety, particularly any dose limiting toxicities. The primary endpoint of the phase 2 part of the study is overall response rate as per IMWG criteria. The dosing cohorts in the dose escalation phase will range from 0.25 mg/kg to 3.68 mg/kg. Given the potential for on-target off-tumor toxicity due to expression of CD38 on non-clonal plasma cells and other hematopoietic cells, blood counts and immunoglobulin levels will be closely monitored. While neurotoxicity or ocular toxicity were not observed with STI-6129 in animal models, including non-human primates, such event will be considered as adverse events of special interest (AESI) and comprehensive neurology and ocular (including slit lamp) examinations will be performed at baseline and study completion, and at any AESI. STI-6129 will be administered intravenously once in a 4-week cycle, with the intention being to treat patients until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Yan: Sorrento Therapeutics: Current Employment. Royal: Sorrento Therapeutics: Current Employment.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal